Definition
Wire wound spirally in order to form coils one on top of the other to make up a coil spring.
Coil springs can be either compression, torsion, extension, or conical springs because all of these springs are made up of helically wound coils of wire. There are many calculations these coil springs have in common when it comes to their physical dimensions but when it comes to spring rate, it can get a little tricky. Especially since conical tapered springs don’t eject a constant force.
Calculations and Formulas
The coil spring calculations that are similar for all springs are the ones shown below. For conical springs, you may do these calculations as well but keep in mind that you might have to do some calculations twice because one of the ends is bigger than the other, therefore the diameters change.
Inner Diameter:
Outer Diameter - 2(Wire Diameter) = Inner Diameter
OD - 2WD = ID

Outer Diameter:
Inner Diameter + 2(Wire Diameter) = Outer Diameter
ID + 2WD = OD
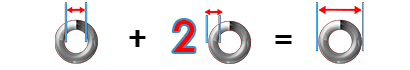
Wire Diameter:
Outer Diameter - Inner Diameter = Wire Diameter
OD - ID = WD
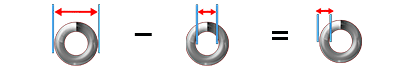
Mean Diameter:
Inner Diameter + Wire Diameter = Mean Diameter
ID + WD = MD
or
Outer Diameter - Wire Diameter = Mean Diameter
OD - WD = MD
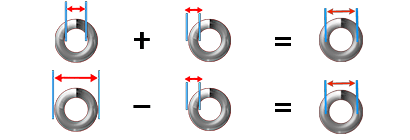
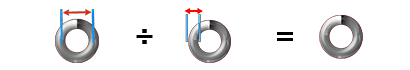
Spring Index:
Mean Diameter ÷ Wire Diameter = Index
MD ÷ WD = I
Total Coils:
Body Length ÷ Wire Diameter - 1 = TC
BL ÷ WD - 1 = TC
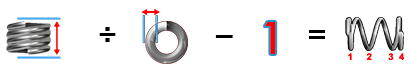
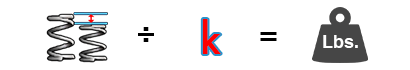
Load:
Rate * Distance Traveled = Load
R(DT) = L
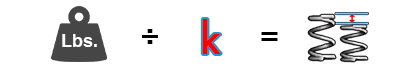
Distance Traveled:
Load ÷ Rate = Distance Traveled
L ÷ R = DT
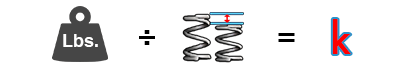
Rate:
Load ÷ Distance Traveled = Rate
L ÷ DT = R

 English
English
